Ms Rdp Client
Use Remote Desktop on your Windows, Android, or iOS device to connect to a Windows 10 PC from afar.
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is a proprietary protocol developed by Microsoft which provides a user with a graphical interface to connect to another computer over a network connection. The user employs RDP client software for this purpose, while the other computer must run RDP server software.
- Install the client. Choose the client that matches the version of Windows. The new Remote Desktop client (MSRDC) supports Windows 10, Windows 10 IoT Enterprise, and Windows 7 client devices.
- Nov 16, 2020 RDP Shortpath is a feature of Windows Virtual Desktop that establishes a direct UDP-based transport between Remote Desktop Client and Session host. RDP uses this transport to deliver Remote Desktop and RemoteApp while offering better reliability and consistent latency.
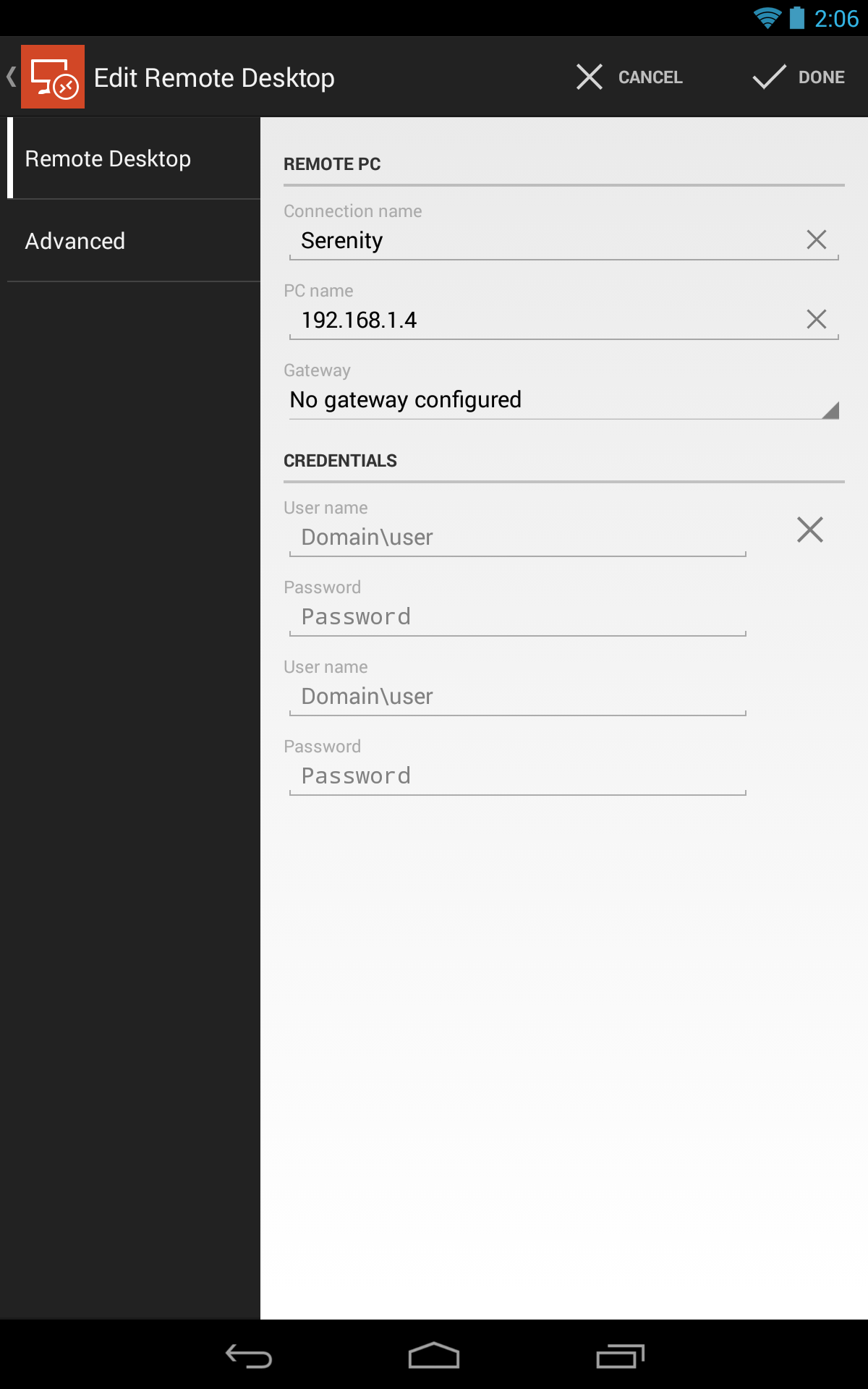
Set up the PC you want to connect to so it allows remote connections:
Make sure you have Windows 10 Pro. To check, go to Start > Settings > System > About and look for Edition. For info on how to get it, go to Upgrade Windows 10 Home to Windows 10 Pro.
When you're ready, select Start > Settings > System > Remote Desktop, and turn on Enable Remote Desktop.
Make note of the name of this PC under How to connect to this PC. You'll need this later.
Use Remote Desktop to connect to the PC you set up:
On your local Windows 10 PC: In the search box on the taskbar, type Remote Desktop Connection, and then select Remote Desktop Connection. In Remote Desktop Connection, type the name of the PC you want to connect to (from Step 1), and then select Connect.
On your Windows, Android, or iOS device: Open the Remote Desktop app (available for free from Microsoft Store, Google Play, and the Mac App Store), and add the name of the PC that you want to connect to (from Step 1). Select the remote PC name that you added, and then wait for the connection to complete.
 -->
-->Important
RDP Shortpath is currently in public preview.This preview is provided without a service level agreement, and we don't recommend using it for production workloads. Certain features might not be supported or might have constrained capabilities.For more information, see Supplemental Terms of Use for Microsoft Azure Previews.
RDP Shortpath is a feature of Windows Virtual Desktop that establishes a direct UDP-based transport between Remote Desktop Client and Session host. RDP uses this transport to deliver Remote Desktop and RemoteApp while offering better reliability and consistent latency.
Key benefits
- RDP Shortpath transport is based on top of highly efficient Universal Rate Control Protocol (URCP). URCP enhances UDP with active monitoring of the network conditions and provides fair and full link utilization. URCP operates at low delay and loss levels as needed by Remote Desktop. URCP achieves the best performance by dynamically learning network parameters and providing protocol with a rate control mechanism.
- RDP Shortpath establishes the direct connectivity between Remote Desktop client and Session Host. Direct connectivity reduces the dependency on the Windows Virtual Desktop gateways, improves the connection's reliability, and increases the bandwidth available for each user session.
- The removal of additional relay reduces the round-trip time, which improves user experience with latency-sensitive applications and input methods.
- RDP Shortpath brings support for configuring Quality of Service (QoS) priority for RDP connections through a Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) marks
- RDP Shortpath transport allows limiting outbound network traffic by specifying a throttle rate for each session.
Connection security
Ms Rdp Client Windows
RDP Shortpath is extending RDP multi-transport capabilities. It doesn't replace reverse connect transport but complements it. All of the initial session brokering is managed through the Windows Virtual Desktop infrastructure.
UDP port 3390 is used only for the incoming Shortpath traffic that is authenticated over reverse connect transport. RDP Shortpath listener ignores all connection attempts to the listener unless they match the reverse connect session.
RDP Shortpath uses a TLS connection between the client and the session host using the session host's certificates. By default, the certificate used for RDP encryption is self-generated by the OS during the deployment. If desired, customers may deploy centrally managed certificates issued by the enterprise certification authority. For more information about certificate configurations, see Windows Server documentation.
RDP Shortpath connection sequence
After installing the reverse connect transport, the client and session host establish the RDP connection and negotiate multi-transport capabilities. Additional steps described below:
- The session host sends the list of its private and public IPv4 and IPv6 addresses to the client.
- The client starts the background thread to establish a parallel UDP-based transport directly to one of the host's IP addresses.
- While the client is probing the provided IP addresses, it continues the initial connection establishment over the reverse connect transport to ensure no delay in the user connection.
- If the client has a direct line of sight and the firewall configuration is correct, the client establishes a secure TLS connection with session host.
- After establishing the Shortpath transport, RDP moves all Dynamic Virtual Channels (DVCs), including remote graphics, input, and device redirection to the new transport.
- If a firewall or network topology prevents the client from establishing direct UDP connectivity, RDP continues with a reverse connect transport.
The diagram below gives a high-level overview of the RDP Shortpath network connection.
Requirements
To support RDP Shortpath, the Windows Virtual Desktop client needs a direct line of sight to the session host. You can get a direct line of sight by using one of the following technologies:
If you're using other VPN types to connect to the Azure virtual network, we recommend using UDP-based VPN for the best results. While the majority of TCP-based VPN solutions encapsulate all IP packets, including UDP, they add inherited overhead of TCP congestion control that would slow down RDP performance.
The direct line of sight means that firewalls aren't blocking UDP port 3390 and the client can connect directly to the session host.
Enabling RDP Shortpath preview
To participate in the preview of RDP Shortpath, you need to enable RDP Shortpath listener on the session host. You can enable RDP Shortpath on any number of session hosts used in your environment. There's no requirement to enable RDP Shortpath on all hosts in the pool.To enable Shortpath listener, you need to configure the following registry values:
Warning
Serious problems might occur if you modify the registry incorrectly using Registry Editor or by using another method. These problems might require that you reinstall your operating system. Microsoft cannot guarantee that these problems can be solved. Modify the registry at your own risk.
On the session host, Start Regedit.exe, and then navigate to the following location:
Create a new DWORD value named fUseUdpPortRedirector and set it to 1 (decimal)
Create a new DWORD value named UdpPortNumber and set it to 3390 (decimal)
Quit Registry Editor.
Restart session host
You can also run the following cmdlets in an elevated PowerShell window to set these registry values:
You can also use PowerShell to configure Group policy
Configure Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security
To allow inbound network traffic for RDP Shortpath, use the Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security node in the Group Policy Management MMC snap-in to create firewall rules.
- Open the Group Policy Management Console to Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security.
- In the navigation pane, select Inbound Rules.
- Select Action, and then select New rule.
- On the Rule Type page of the New Inbound Rule Wizard, select Custom, and then select Next.
- On the Program page, select This program path, and type '%SystemRoot%system32svchost.exe' then select Next.
- On the Protocol and Ports page, select the UDP protocol type. In the Local port, select 'Specific ports' and type in 3390.
- On the Scope page, you can specify that the rule applies only to network traffic to or from the IP addresses entered on this page. Configure as appropriate for your design, and then select Next.
- On the Action page, select Allow the connection, and then select Next.
- On the Profile page, select the network location types to which this rule applies, and then select Next.
- On the Name page, type a name and description for your rule, and then select Finish.
You can verify that the new rule matches the screenshots below:
You can also use PowerShell to configure Windows Firewall:
Using PowerShell to configure Windows Defender Firewall
You can also use PowerShell to configure Group policy
Configuring Azure Network Security Group
To allow access to the RDP Shortpath listener across network security boundaries, you need to configure Azure Network Security Group to allow inbound UDP port 3390.Follow the network security group documentation to create an inbound security rule allowing traffic with following parameters:
- Source - Any or the IP range where the clients are residing
- Source port ranges - *
- Destination - Any
- Destination port ranges - 3390
- Protocol - UDP
- Action - Allow
- Optionally change the Priority. The priority affects the order in which rules are applied: the lower the numerical value, the earlier the rule is applied.
- Name - - RDP Shortpath
Disabling RDP Shortpath for a specific subnet
If you need to block specific subnets from using the RDP Shortpath transport, you can configure additional network security groups specifying the Source IP ranges.
Verifying the connectivity
Using Connection Information dialog
To verify that connections are using RDP Shortpath, open the “Connection Information” dialog by clicking on the antenna icon in the connection toolbar.
Using event logs
To verify that session is using RDP Shortpath transport:

- Connect to the desktop of the VM using Windows Virtual Desktop client.
- Launch the Event Viewer and navigate to the following node: Applications and Services Logs > Microsoft > Windows > RemoteDesktopServices-RdpCoreCDV > Microsoft-Windows-RemoteDesktopServices-RdpCoreCDV/Operational
- To determine if RDP Shortpath transport is used, look for event ID 131.
Using Log Analytics to verify Shortpath connectivity
If you are using Azure Log Analytics, you can monitor connections by querying the WVDConnections table. A column named UdpUse, indicates whether Windows Virtual Desktop RDP Stack uses UDP protocol on current user connection.The possible values are:
- 0 - user connection isn't using RDP Shortpath
- 1 - user connection is using RDP Shortpath
The following query list lets you review connection information. You can run this query in the Log Analytics query editor. For each query, replace userupn with the UPN of the user you want to look up.
Online Rdp Client
Troubleshooting
Verify Shortpath listener
To verify that UDP listener is enabled, use the following PowerShell command on the session host:
If enabled, you'll see the output like the following
If there is a conflict, you can identify the process occupying the port using the following command
Disabling RDP Shortpath
Apple Ms Rdp Client
In some cases, you may need to disable RDP Shortpath transport. You can disable RDP Shortpath by using the group policy.
Disabling RDP Shortpath on the client
To disable RDP Shortpath for a specific client, you can use the following Group Policy to disable the UDP support:
- On the client, Run gpedit.msc.
- Navigate to Computer Configuration > Administration Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Connection Client.
- Set the “Turn Off UDP On Client” setting to Enabled
Disabling RDP Shortpath on the session host
Ms Rdp Client Software
To disable RDP Shortpath for a specific session host, you can use the following Group Policy to disable the UDP support:
Ms Rdp Client App

- On the Session Host Run gpedit.msc.
- Navigate to Computer Configuration > Administration Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Connection Host > Connections.
- Set the “Select RDP Transport Protocols” setting to TCP Only
Public preview feedback
We'd like to hear from you about your experiences with this public preview!
- For questions, requests, comments, and other feedback, use this feedback form.
Next steps
- To learn about Windows Virtual Desktop network connectivity, see Understanding Windows Virtual Desktop network connectivity.
- To get started with Quality of Service (QoS) for Windows Virtual Desktop, see Implement Quality of Service (QoS) for Windows Virtual Desktop.
